brinell hardness test aluminum|brinell hardness chart for aluminum : mail order Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, . Resultado da Kerolay Chaves (@kerolay_chaves1) on TikTok | 22.3M Likes. 2.4M Followers. Oii, tenho 22 aninhos 🙈 MEU INST4: só clicar no quadrado↗️ LIVE SEMPRE LÁ.Watch the latest video from Kerolay Chaves (@kerolay_chaves1).
{plog:ftitle_list}
webO caso “não me mate meu irmão portal zacarias” é um desses eventos que chocou profundamente a sociedade e desencadeou uma onda de choque e compaixão em todo o mundo. Trata-se de uma história de horror que transcende os limites da imaginação e ilustra a profundidade da maldade humana.
The hardness of aluminum can be assessed through various testing methods, including Brinell hardness and Rockwell hardness. The hardness of aluminum alloys is related to the other metals they are alloyed . The Brinell hardness test is commonly used to determine the hardness of materials .When quoting a Brinell hardness number (BHN or more commonly HB), the conditions of the test used to obtain the number must be specified. The standard format for specifying tests can be seen in the example "HBW 10/3000". "HBW" means that a tungsten carbide (from the chemical symbol for tungsten or from the Spanish/Swedish/German name for tungsten, "Wolfram") ball indenter was used, as opposed to "HBS", which means a hardened steel ball. The "10" is the ba.
According to ISO 6506, the spherical indenter made of hard metal (tungsten carbide) is pressed into a specimen (workpiece) with a defined test load (between 1 kgf and 3000 kgf) to determine the Brinell hardness (HBW).Brinell hardness testing is a commonly used method for determining the hardness of metals and alloys. The Brinell hardness test formula. When measuring hardness using the Brinell method, . ASTM E10-18. Standard Test Method for Brinell Hardness of Metallic Materials. Significance and Use. 4.1 The Brinell hardness test is an indentation hardness test that can .The Brinell test is typically used for materials with a coarse or granular microstructure, such as cast iron, aluminium, and soft metals. It provides a reliable measurement of hardness but may not be suitable for very hard or thin .
The Brinell hardness test is a commonly used hardness testing method that measures the hardness of materials. It does so by pressing a hard ball indenter into the surface of the material under a specified load and . Brinell hardness testing is typically used in testing aluminum and copper alloys (at lower forces) and steels and cast irons at the higher force ranges.Here are some of the most common hardness tests used in the industry to ascertain the hardness of Aluminum. Brinell Hardness Test. This test uses an indenter with huge loads making it suitable for very thick, large, and rough-grained material surfaces. The indenter is a carbide ball with a diameter ranging between 1 – 10mm, and its load can .Applications for Brinell Methods Brinell testing is suitable for measuring the hardness of rela-tively soft materials, including low-carbon steels, aluminum, lead, copper, and some plastics. The use of a large indenter and high load helps to minimize the effect of surface irregu-larities and yields more accurate hardness values. Soft Materials .
For softer materials or materials with coarse microstructures – the Brinell hardness test is suitable. . Hard anodised parts are tested for hardness using the Vickers test. On average, hard anodised aluminium 6082 can achieve .Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .
These approximate relationships between hardness and tensile strength do not apply to nonferrous metals, with the possible exception of certain aluminum alloys. Related: Brinell Hardness Testing Equation. Table A Brinell Hardness to . The Brinell hardness test is ideal for measuring the hardness of metals with coarse or inhomogeneous grain structures, such as cast iron and softer metals like aluminum alloys. It measures the diameter of a larger indentation, which averages out variations in the material’s microstructure, providing a more representative hardness value for . General Information about the Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell hardness test involves pressing a hard ball indenter, usually made of tungsten carbide, into the material’s surface with a specified force. The diameter of the ball is typically 10 mm, but smaller diameters such as 2.5 mm can also be used for specific applications.
The Brinell hardness test records the diameter and depth of the indentation caused by a ball-shaped indenter, with the indenter pressed into a material's surface. This is the guide on how to read and represent brinell hardness values. . The hardness number for pure aluminum is fifteen, while the hardness number for hardened aluminum is . Prosedur Hardness Test : 1. Brinell Hardness Test. Hal yang perlu diperhatikan pada saat pengujian hardness Brinell adalah sebagai berikut : Spesimen harus memenuhi persyaratan : – Rata dan halus. – Ketebalan minimal 6 mm. – Bisa ditumpu dengan baik dan permukaan uji harus horizontal. These heat-treated samples were then tested mechanically using the Brinell hardness test (BH). . Aluminum Matrix Composites (AMC) are frequently employed to meet industrial requirements. In this .
The Brinell hardness test method as used to determine Brinell hardness, is defined in ASTM E10. Most commonly it is used to test materials that have a structure that is too coarse or that have a surface that is too rough to be tested using another test method, e.g., castings and forgings. Brinell testing often use a very high test load (3000 .
Brinell hardness of 6061 aluminium alloy depends greatly on the temper of the material, but for T6 temper it is approximately 95 MPa. Facebook Instagram Youtube Twitter . . Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester .Brinell hardness of 6061 aluminium alloy depends greatly on the temper of the material, but for T6 temper it is approximately 105 MPa. Rockwell hardness test is one of the most common indentation hardness tests, that has been developed for hardness testing. In contrast to Brinell test, the Rockwell tester measures the depth of penetration of an .
The Brinell hardness test uses a hardened steel ball indenter that is pushed into the material under a specified force. . The XXX is the force to apply (in kgf) on a material of type YY (5 for aluminum alloys, 10 for copper alloys, 30 for steels). Thus a typical steel hardness could be written: 250 HB 30D2. It could be a maximum or a minimum .
DEFINITION OF THE BRINELL HARDNESS TEST The Brinell hardness test was originally developed in the late 1800s by the Swedish engineer of the same name. He wanted to find a method to control the quality/hardness of steel. His .10.5.2 Performance-testing methods for aluminum alloys. . For example, Brinell Hardness (HB) test is expressed by the pressure loaded on the press mark per unit area. The hardness of natural minerals is often tested by scratch hardness. Mineral hardness is divided into 10 grades, and the increasing order is: talc, gypsum, calcite, fluorite .Brinell Hardness Test. The Brinell test uses a larger spherical indenter, usually made of steel or carbide, and applies a heavy load to the material. . For example, steel may have a more straightforward conversion, but materials like aluminum or composite metals may require more precise testing to avoid conversion errors. 3. Account for Load .
using western digital diagnostics to test hard drive
The Brinell hardness test method follows ASTM E10 standards to inspect the materials whose structure is too coarse or having a rough surface such as castings and forgings. . the Brinell hardness test can be applied to metals like copper and aluminum using low forces and cast irons and steel with higher force. Also, the application of high .Though loads of 500, 1000, 1500, 2000, 2500, and 3000 N are available in a typical Brinell hardness tester, a load of 500 N is used for testing relatively soft metals such as copper and aluminium alloys, while the 3000 N load is often used for testing harder materials such as steels and cast irons.However, the general rule is that the combination of test load and ball diameter .Aluminum alloys are generally softer than other metals, such as steel or titanium. However, the hardness of aluminum alloys can vary widely depending on the alloying elements present and the heat treatment process used. The following tables provide a list of Brinell hardness (HB) values for common aluminum alloys.
When the Brinell hardness test cannot be used, such as when the material’s HB value is greater than 450 or the sample size is too small, the Rockwell hardness test is used instead. This test involves pressing either a diamond cone with a top angle of 120° or a steel ball with a diameter of 1.59 mm or 3.18 mm into the surface of the tested . The article covers data on the Brinell hardness of the forged precipitation-hardened aluminum alloy EN AW-2618A in the initial T61 condition (i. e. slightly underaged) and after isothermal aging for up to 25,000 h at aging temperatures between 160 °C and 350 °C.The data obtained by Brinell hardness test with the tungsten carbide ball “HBW” and non – standardized hardened steel ball “HBS” measured by 8 appraisers were compared by Youden plot, MSA, analysis of uncertainty, t-test and analysis of variance (ANOVA). . This procedure was repeated by group A1, in testing the hardness of an .and Rockwell superficial hardness of wrought aluminum prod-ucts. 1.10 Many of the conversion values presented herein were . both the Rockwell and Brinell hardness standards (Test Method E 18 and E 10, respectively) allow or require the use of tungsten carbide ball indenters; however, all of the ball scale Rockwell hardness tests (HRB, .
1.5 At the time the Brinell hardness test was developed, the force levels were specified in units of kilograms-force (kgf). Although this standard specifies the unit of force in the International System of Units (SI) as the Newton (N), because of the historical precedent and continued common usage of kgf units, force values in kgf units are provided for information . The Brinell hardness test consists of applying a constant load or force, usually between 187.5 and 3000Kgf, for a specified time (from 10 – 30 seconds) typically using a 2.5 or 10mm diameter tungsten carbide ball (see schematic in the image to your right – Figure 23.3). . Brinell hardness testing is typically used in testing aluminum and .
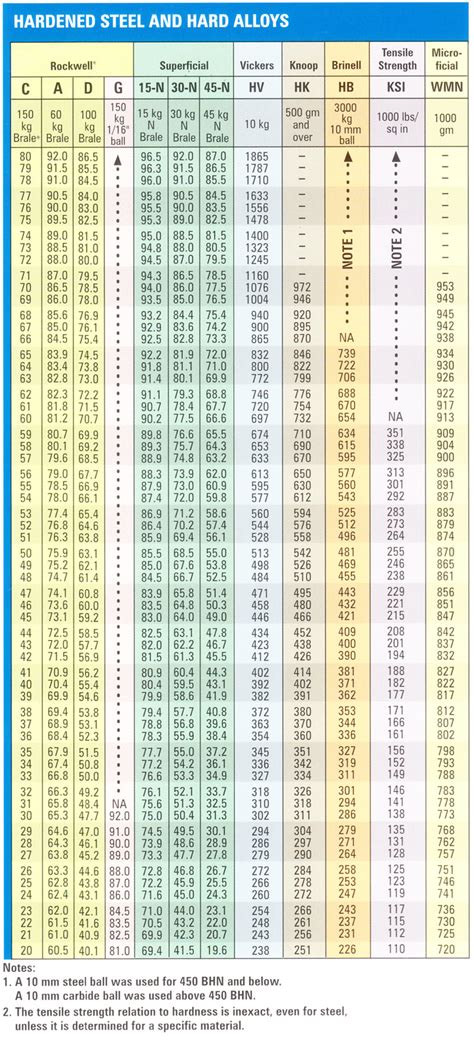
rockwell hardness scale for aluminum
rockwell hardness chart for aluminum
Resultado da Alwin GC. 10,465 likes · 106 talking about this. FREE ‘Happiness Tracker’
brinell hardness test aluminum|brinell hardness chart for aluminum